Key Takeaways
- A multi-party computation (MPC) wallet enables holders to store their crypto assets safely by dividing secret keys between parties using secret codes that are kept safe from everyone else.
- MPC wallets are becoming more popular within the crypto space because of their advanced security relative to older methods like hot wallets, cold wallets and hardware wallets.
- Each of the MPC wallet parties holds its own asset data, which allows it to perform transactions without revealing the data it holds to other holders.
- Multi-party computation uses cryptographic methods to ensure data privacy and accuracy, thereby preventing breaches even when a party deviates from the protocol.
While multi-party computation technology has been around for a while, the increase of applications requiring increased security, better user experiences and streamlined transactions has made them popular in the crypto space. As EVM-compatible blockchains pave the way for Web3 wallets where smart accounts demand form smarter wallets like MPC wallets, we walk you through the concept of an MPC wallet technology, how it works, its primary benefits, and the role it plays in digital asset security within the finance industry.
MPC Wallet Technology
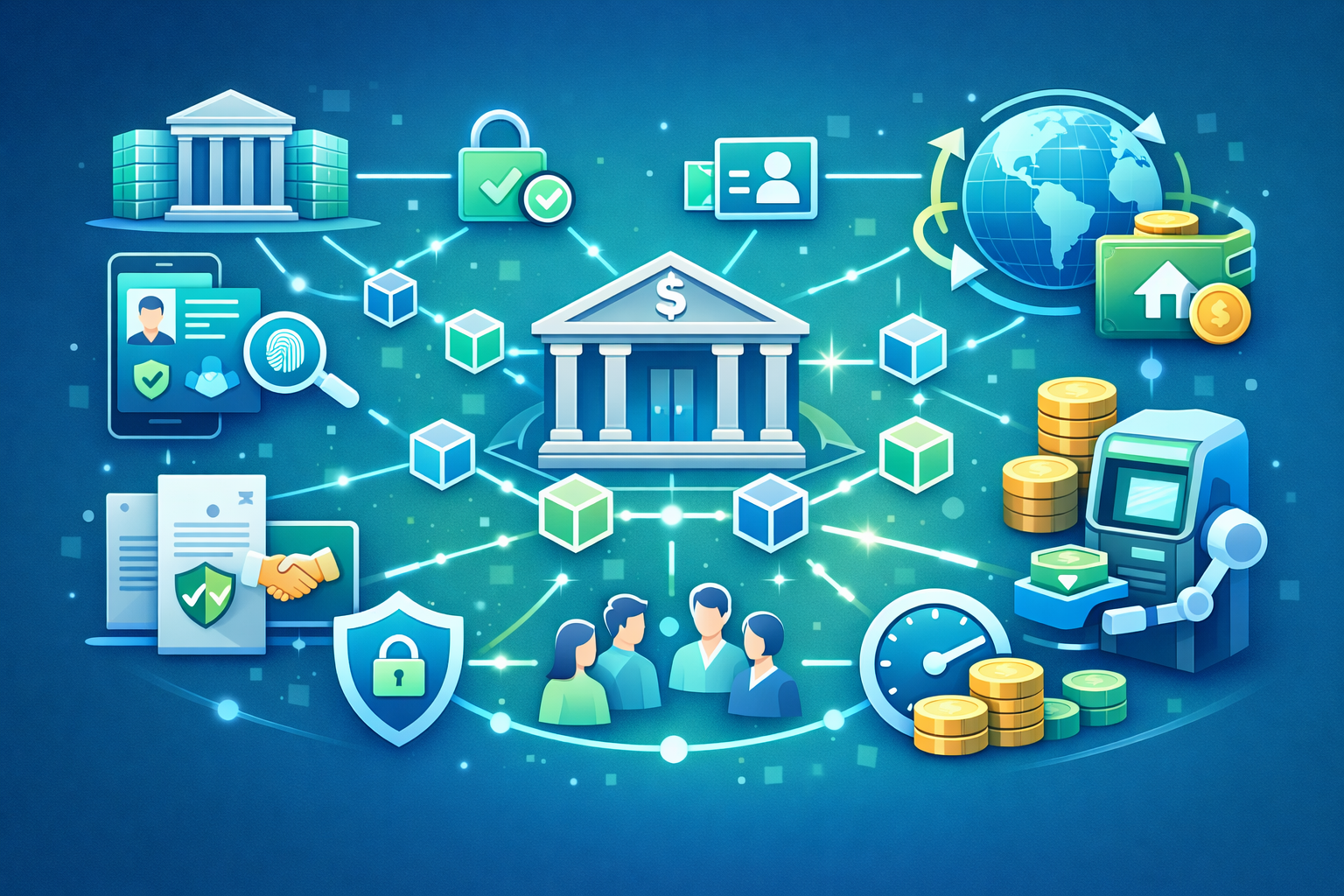
The MPC (Multi-party computation) wallet plays a significant role in guaranteeing privacy in situations where maintaining strict data confidentiality is a minimum. The wallet is a primary technology in securing and transferring digital assets by enabling multiple parties to compute functions without revealing personal inputs to the other parties.
Multi-party Computation (MPC) consists of a set of cryptographic protocols that enable multiple parties to evaluate a function together, with each party securely holding their private data without revealing it to the other parties. When applied within a digital wallet, MPC splits and shares parts of the private keys and stores them in different locations owned by different users without revealing the complete private key. In crypto, MPC integrates public-key cryptography to collaboratively sign transactions to eliminate single points of failure since no single entity has access to the entire private key.
Functionality and Operation
Also known as the Secure MPC Wallet (SMPC), the wallet differs from single-key wallets, whose one private key can easily be lost or stolen. Also, unlike multi-signature wallets that are cumbersome and rely on multiple signatures, a factor that can affect a wallet’s availability in time-sensitive situations, an MPC wallet is more secure and protocol-agnostic as it maintains the signer’s privacy.
MPC wallets use a cryptographic technique that splits the traditional private key into multiple shares, which it distributes to involved parties, including users and private servers. Whenever a transaction requires signing, the parties team up to generate the signature without recreating the entire private key.
Once someone initiates a transaction, the parties, in this case, the user and their wallet provider’s server, open an MPC protocol with which they will jointly sign the transaction. Both parties individually hold a piece of the private key, with which they compute their share of the signature.
The parties create a valid signature to authorize the transaction by combining their private key shares. The private key shares are never exposed throughout the process, meaning none of the parties will access the other’s share. As a result, no third party can gain full control of the SMPC wallet or its contents, even if they successfully compromised one party.
Benefits for Investors, Developers, and Finance Professionals
Multi-party computation (MPC) wallets provide benefits that include flexibility and control that enable transactional parties to participate in the management of their assets jointly. The wallets’ features are especially significant when efficient asset management and transfer, risk mitigation, and streamlined collaboration between parties are paramount. Among the tangible benefits of using a secure MPC wallet include:
Enhanced Security: Distributing private keys into multiple shares among different parties reduces the chances of unauthorized access or theft of digital assets.
Better-quality Access Control and Permissions: Secure MPC wallets facilitate more granular access and permission settings. Multiple users, especially in organizational settings, can clearly define every participant’s roles and responsibilities.
Efficient Collaboration and Decision-making: Multiple parties must sign off on transactions, which encourages collaboration and shared decision-making. This can prevent unauthorized transactions and ensure that every stakeholder is involved in important decisions.
Support Complex Transaction Requirements: A multi-party computation wallet accommodates sophisticated transactional needs. This can include multi-step approvals, time-locking, and spending limits, especially within organizations with compliance requirements and complex financial operations.
Compliance: MPC wallets are compatible with global regulations and financial industry standards regarding digital asset custody. Wallet users can employ Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) requirements to verify sources of funds or identities before authorizing transactions. The availability of transaction logs and records makes it easy for users to adhere to financial reporting, audit obligations, or other industry best practices associated with governance and security using industry policies and procedures.
Use Cases and Applications of MPC Wallets
The SMPC wallet technology offers institutional-grade custodial solutions for organizations involved with digital assets. Some examples of how different organizations are using MPC wallets within the industry include the following:
Institutional Asset Management: Financial institutions managing large digital asset portfolios increasingly adopt multi-party computational wallets. The wallet’s enhanced security features make it the go-to solution for institutional investors who must safeguard their colossal cryptocurrency investments against fraud or external cyber threats.
Cross-Organizational Financial Transactions: Partnerships, joint ventures, and consortiums whose workings require cross-organizational financial transactions repeatedly choose SMPC wallets. The wallets allow seamless collaborative transactions while ensuring all parties’ data remain private.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Platforms: MPC wallets are well-suited for DeFi operations. They enhance security operations by offering a secure way to manage the private keys required to execute smart contracts. This helps mitigate the risk of private key management or theft of digital assets in DeFi operations.
Cryptocurrency Custody Solutions: Organizations offering cryptocurrency custody services increasingly turn to multi-party computation wallets, which provide robust security for their client’s digital assets. MPC guarantees clients that their crypto assets are safe from internal or external threats.
Future Implications and Trends for MPC Wallets
Recent developments in the blockchain and crypto space indicate increasing interest and potential adoption within the mainstream financial sector. With the increased possibility of traditional financial institutions like banks, hedge funds, and other entities adopting crypto, there are more possibilities for such organizations to turn to MPC wallets to manage their crypto assets securely.
Ongoing research and advancements in cryptographic techniques will also positively impact the MPC wallet sector, leading to more robust and efficient protocols. The advancements will help reduce computation overheads and other costs associated with using MPC wallets and enhance transaction speeds and scalability.
The potential introduction of interoperability and cross-chain functionality to enable users to manage their crypto assets flawlessly across different blockchains will be a big plus for SMPC wallets. As the technology continues to evolve, we expect to see improved user interfaces and experience to make the wallets more accessible and easy to use by broader audiences.
Multi-party computation technology is also likely to expand beyond crypto and find applications in numerous other sectors where secure, collaborative computation is required. Some examples that come to mind include secure logistics in supply chains or the need to manage sensitive data, such as in the healthcare industry.
MPC wallet technology could soon find a place in mobile devices and the Internet of Things (IoT) applications as they could provide secure transaction capabilities. However, for that to happen effectively, MPC wallet developers must enhance the existing privacy features to allow users to execute transactions with greater anonymity. Also, they could create wallets offering customizable security features and policies that enable users to tailor settings to their specific needs based on their operational contexts.
With their distributed key management using advanced cryptographic techniques, MPC wallets have emerged as sophisticated solutions in cryptocurrency security. These institutional-grade digital asset wallets use Multi-Party Computation technology to enable multiple parties to jointly compute a private key without revealing their respective inputs. SMPC wallets offer military-grade storage and transaction security for digital assets and are preferred by institutions where financial compliance rules require multiple signatories to approve transactions. While they may still have a few limitations, SMPC wallets have advantages in terms of enhanced privacy, security, and reduced reliance on conventional crypto storage methods.
Conclusion
Besides offering enhanced protection against cyber threats, MPC wallets embody the core elements of blockchain technology, like decentralization and efficiency. As the ever-dynamic blockchain and cryptocurrency sectors evolve, multi-party computation wallets could become integral to crypto asset management. The role of multi-party computation wallets also increases beyond the current crypto-based applications. It has become a key player in shaping a secure future for trust-based crypto transactions and digital assets management.